I. Introduction:
In today’s rapidly evolving world, the significance of sustainable solutions for enhanced efficiency cannot be overstated. As we strive towards a greener and more sustainable future, it is crucial to leverage the power of technology to achieve our sustainability goals. One such technological advancement that plays a key role in this endeavour is the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and automation. By harnessing the potential of these cutting-edge technologies, organizations can optimize their processes, improve productivity, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction.
II. Understanding IoT and Automation:
Before delving into the countless possibilities IoT and automation offers, it is essential to understand these concepts and their relevance to sustainability. The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the network of interconnected physical devices embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to collect and exchange data. These devices can range from everyday objects like smart thermostats and wearables to complex machinery in industrial sectors. The beauty of IoT lies in its ability to seamlessly connect and communicate, allowing for data-driven decision-making and automation. Automation, on the other hand, involves the use of technology to streamline and optimize various processes. It eliminates the need for manual intervention by relying on machines and algorithms to execute tasks efficiently and with high precision. Organizations can drastically increase productivity and reduce waste by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks.
III. Leveraging IoT for Sustainable Solutions:
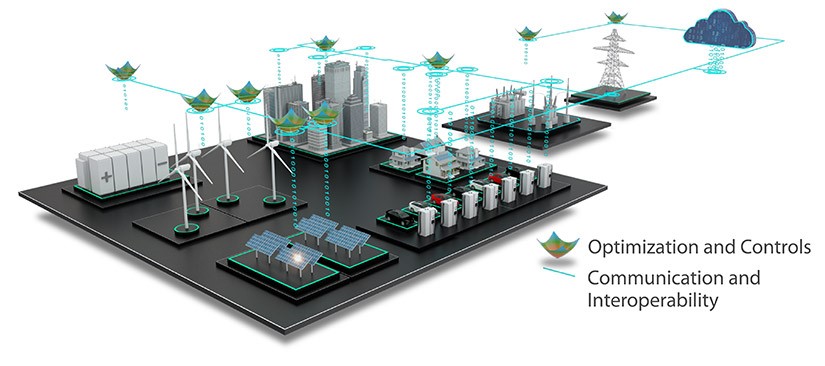
A. IoT Applications in Energy Conservation:
1. Smart grid systems and their impact on energy consumption
Smart grid systems utilize IoT technology to monitor and analyse energy consumption patterns in real time. By capturing data from millions of smart meters, these systems provide valuable insights that help utility companies optimize the distribution of electricity. This not only minimizes energy wastage but also improves the overall reliability and resilience of the grid.
2. Optimizing energy usage through IoT-enabled devices
IoT-enabled devices, such as smart thermostats and appliances, empower individuals to monitor and control their energy consumption. By remotely adjusting temperatures or scheduling appliance usage based on energy demand, consumers can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and lower their energy bills.
B. IoT-driven Waste Management:

1. Effective waste collection using IoT sensors and real-time monitoring
IoT sensors installed in waste bins can monitor fill levels, and temperature, and even detect potential leaks or hazardous materials in real-time. This enables waste management companies to optimize collection routes, reducing unnecessary trips and emissions. Additionally, smart waste bins equipped with sensors can send alerts when they are nearing full capacity, ensuring timely collection and preventing overflowing bins.
2. Implementing smart recycling systems for sustainable waste management
IoT technology can enable the intelligent sorting of recyclable materials by analysing their composition and sorting them accurately. Automated sorting machines, guided by machine learning algorithms, ensure that materials are allocated to the appropriate recycling streams. This not only enhances recycling efficiency but also reduces contamination, leading to a more sustainable waste management process.
IV. Automation for Enhanced Efficiency
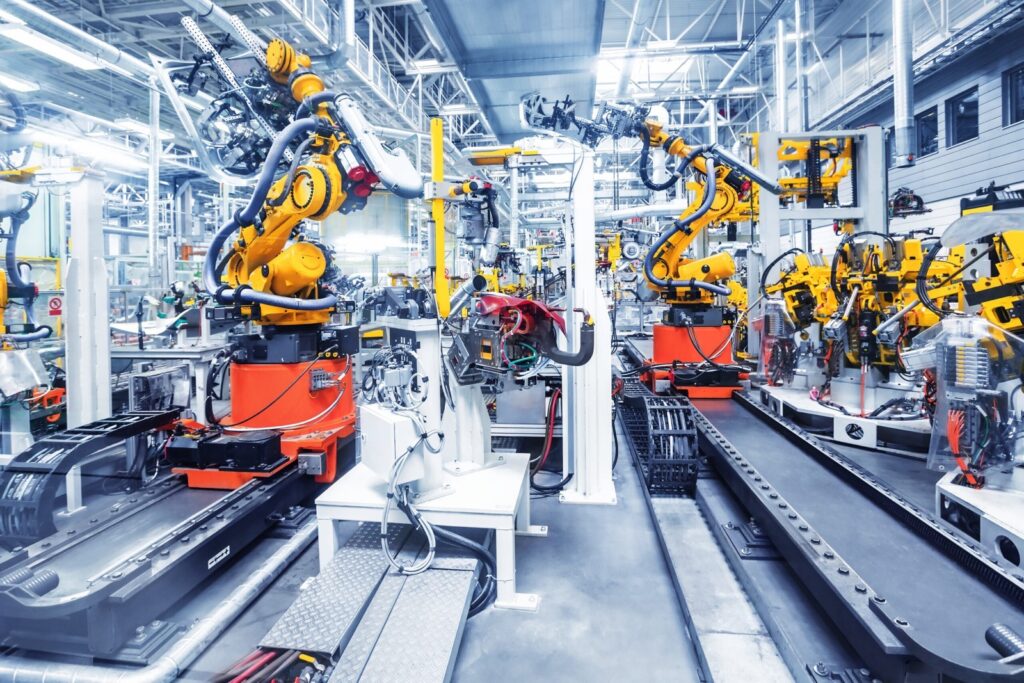

A. Streamlining Industrial Processes:
1. Automating manufacturing processes for increased productivity and reduced waste
Automation plays a vital role in modern manufacturing, revolutionizing production lines and assembly processes. By replacing manual labour with robots and utilizing AI technologies, organizations can achieve higher levels of efficiency, precision, and consistency. This not only leads to increased productivity but also reduces waste, as automation minimizes human error and optimizes resource utilization.
2. Robotics and AI technologies in industrial automation
Robotics and AI technologies are transforming the manufacturing landscape. From automated guided vehicles (AGVs) that streamline logistics within factories to collaborative robots (cobots) that work alongside humans, these advancements are paving the way for enhanced efficiency and flexibility in industrial processes. The ability of these technologies to adapt and learn from data further enhances productivity and sustainability.
B. Intelligent Building Management:

1. The role of automation in energy-efficient building operations
Automation is revolutionizing the way buildings are managed, making them more energy-efficient and sustainable. Automated systems can regulate lighting, heating, and cooling based on occupancy patterns, optimizing energy consumption. Additionally, smart building management platforms enable real-time monitoring and analysis of energy usage, empowering facility managers to identify inefficiencies and implement improvements.
2. Smart HVAC systems for optimized energy consumption
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems account for a significant portion of energy consumption in buildings. Integrating IoT sensors and automation allows HVAC systems to operate more intelligently, adjusting temperature settings based on real-time occupancy and external factors. This not only enhances comfort but also reduces energy waste, ultimately leading to substantial energy savings.
C. Automating Supply Chain and Logistics:

1. Enhancing efficiency and sustainability through automated logistics
Automation is reshaping the logistics industry, revolutionizing the way goods are transported, tracked, and delivered. Autonomous vehicles, drones, and warehouse robots enable faster, more accurate, and cost-effective operations. By optimizing routes and reducing idling time, automated logistics systems minimize fuel consumption, emissions, and overall environmental impact, contributing to a more sustainable supply chain.
2. IoT-enabled inventory management and predictive analytics
By leveraging IoT sensors and automation, businesses can gain real-time visibility into their inventory levels, leading to improved demand forecasting and enhanced supply chain management. Predictive analytics algorithms can analyse historical and real-time data to identify trends, minimize stockouts, and optimize inventory levels. This reduces waste and storage costs and enables organizations to respond swiftly to changing market dynamics.
V. The Benefits and Barriers of IoT and Automation
A. Benefits of IoT and Automation:
1. Reduced energy consumption and resource optimization
By combining IoT technology and automation, organizations can significantly reduce energy consumption through optimized processes and proactive resource management. This not only leads to cost savings but also diminishes the environmental impact, promoting sustainability on a larger scale.
2. Improved productivity and cost savings
Automation eliminates manual processes, reducing the risk of human error and increasing overall productivity. Organizations can allocate resources more efficiently and achieve cost savings by streamlining operations. The ability of IoT to provide real-time data and insights enables data-driven decision-making, further enhancing productivity and driving business growth.
B. Challenges and Barriers to Implementation:
1. Security and privacy concerns
As the integration of IoT and automation becomes more prevalent, security and privacy concerns become significant challenges. IoT devices are potential targets for cyberattacks, and organizations must ensure robust security measures are in place to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, privacy concerns arise from the vast amount of personal data collected by IoT devices, raising ethical questions that need careful consideration.
2. Workforce skills and training requirements
The shift towards IoT and automation necessitates upskilling or reskilling the existing workforce to handle these advanced technologies. Organizations must invest in providing adequate training and education to bridge the skills gap. Additionally, the fear of job displacement due to automation poses a barrier to adoption and requires proactive measures to address the concerns of employees.
VI. Case Studies: Successful Implementations
A. Sustainable Smart Cities
1. Examining how smart cities leverage IoT for enhanced sustainability
Smart cities leverage IoT technology to create more sustainable and efficient urban environments. From intelligent street lighting that adjusts brightness based on traffic density to smart waste management systems that optimize collection routes, IoT plays a vital role in transforming cities into sustainable ecosystems.
2. Examples of successful smart city projects

•Barcelona, Spain: The city implemented an IoT-powered irrigation system that uses sensors to monitor soil moisture levels and adjust watering schedules, leading to a significant reduction in water consumption.
•Singapore: The city-state uses a comprehensive suite of IoT solutions to optimize energy usage, monitor traffic flow, and enhance waste management. This has resulted in improved sustainability and liveability for its residents.
B. Industrial Automation Success Stories
1. Real-life examples of automation transforming industries

•Tesla: The automotive company utilizes automation extensively in its manufacturing process, resulting in higher production rates and improved quality control.
•Amazon: The e-commerce giant employs a vast network of robots in its warehouses, automating the picking, packing, and shipping processes. This has led to faster order fulfilment and improved customer satisfaction.
VII. Future Trends and Innovations
In the field of IoT and automation, continuous innovation is driving the sustainability agenda forward. Some emerging trends and innovations to look out for include:

1. Edge computing: Processing and analysing data closer to the source, reducing latency and enhancing efficiency.
2. Artificial intelligence and machine learning: These technologies are expected to further optimize automation and enable more intelligent decision-making.
3. 5G connectivity: The implementation of 5G networks will provide faster and more reliable connectivity, unlocking new possibilities for IoT applications.
4. Blockchain: This technology can enhance security and transparency in IoT systems, facilitating secure data sharing and transactions.
5. Circular economy integration: Leveraging IoT and automation to support the transition to a circular economy, where resources are kept in use for as long as possible.
VIII. Conclusion
To achieve enhanced efficiency and sustainability in various sectors, harnessing the power of IoT and automation is crucial. The integration of these technologies enables energy conservation, waste management optimization, streamlined industrial processes, intelligent building management, and efficient supply chain operations. While there may be challenges and barriers to overcome, the benefits in terms of reduced energy consumption, improved productivity, and cost savings are substantial. By learning from successful implementations and embracing future trends and innovations, we can pave the way for a greener and more sustainable future.
IX. FAQs:
1. What is the significance of sustainable solutions in today’s world?
Sustainable solutions are vital to addressing environmental challenges and preserving the planet for future generations. They promote responsible resource use, reduce carbon emissions, and foster economic growth.
2. How does IoT contribute to enhancing efficiency in various sectors?
IoT provides real-time data and insights, enabling proactive decision-making and process optimization. It enhances energy conservation, waste management, transportation efficiency, and overall productivity.
3. What are the potential challenges in implementing IoT and automation?
Security and privacy concerns, workforce skills and training requirements, and potential job displacement are some challenges organizations may face during the implementation of IoT and automation.
4. Can you provide examples of successful sustainable smart city projects?
Barcelona’s IoT-powered irrigation system and Singapore’s comprehensive suite of IoT solutions for energy optimization and waste management are successful smart city projects.
5. What are the future trends and innovations anticipated in this field?
Future trends include edge computing, AI and machine learning, 5G connectivity, blockchain integration, and leveraging IoT and automation for the circular economy.
In conclusion, harnessing the potential of IoT and automation is essential in achieving sustainable solutions for enhanced efficiency. By adopting these technologies in various sectors, we can make significant progress towards a greener and more sustainable future. The benefits of reduced energy consumption, improved productivity, and cost savings outweigh the challenges, and continuous innovation will further drive the sustainability agenda forward. Embracing these advancements and learning from successful implementations will pave the way for a better world for generations to come.